1.5. Lifecycle of a Release
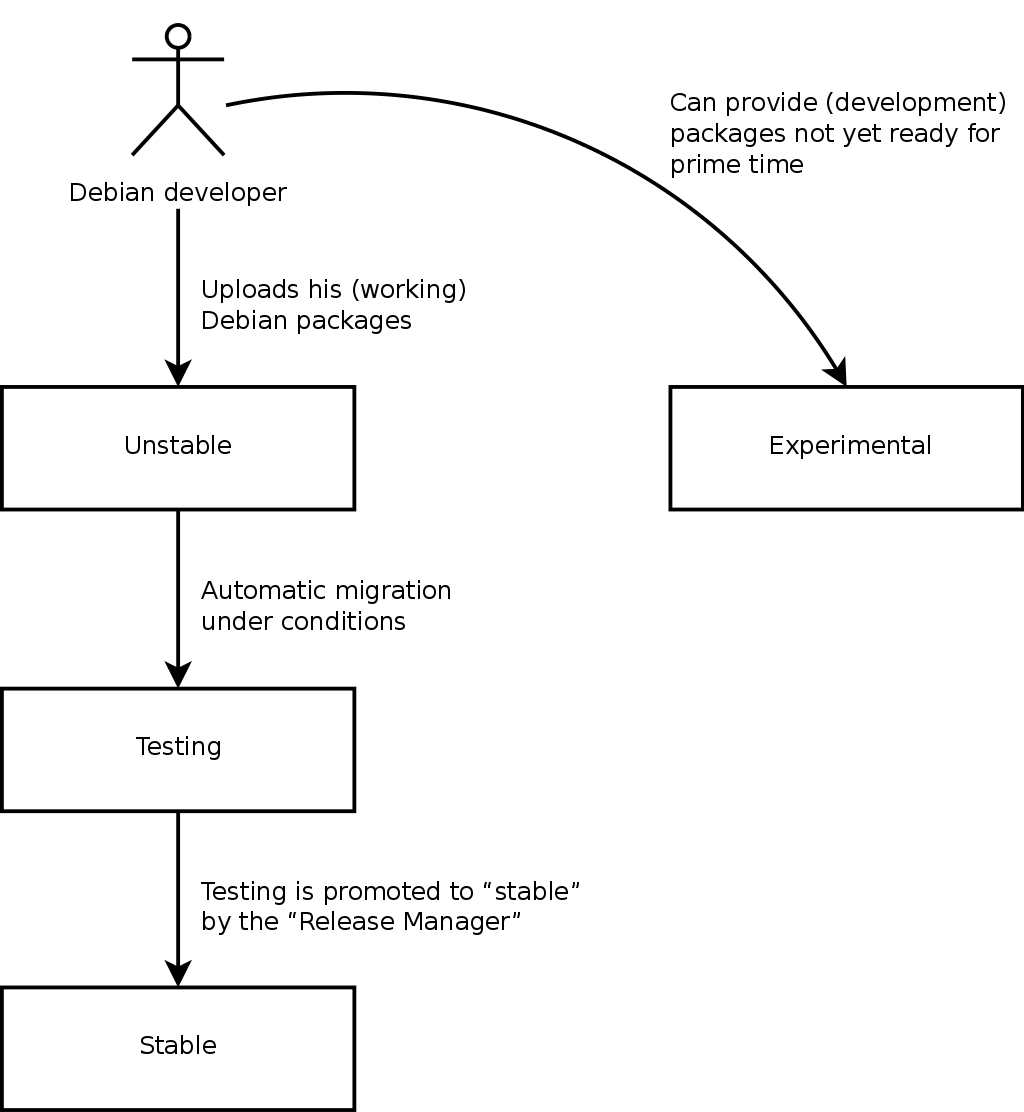
The project will simultaneously have three or four different versions of each program, named
Experimental,
Unstable,
Testing, and
Stable. Each one corresponds to a different phase in development. For a good understanding, let us take a look at a program's journey, from its initial packaging to inclusion in a stable version of Debian.
1.5.1. The Experimental Status
First let us take a look at the particular case of the
Experimental distribution: this is a group of Debian packages corresponding to the software currently in development, and not necessarily completed, explaining its name. Not everything passes through this step; some developers add packages here in order to get feedback from more experienced (or braver) users.
Otherwise, this distribution frequently houses important modifications to base packages, whose integration into
Unstable with serious bugs would have critical repercussions. It is, thus, a completely isolated distribution, its packages never migrate to another version (except by direct, express intervention of the maintainer or the ftpmasters).
1.5.2. The Unstable Status
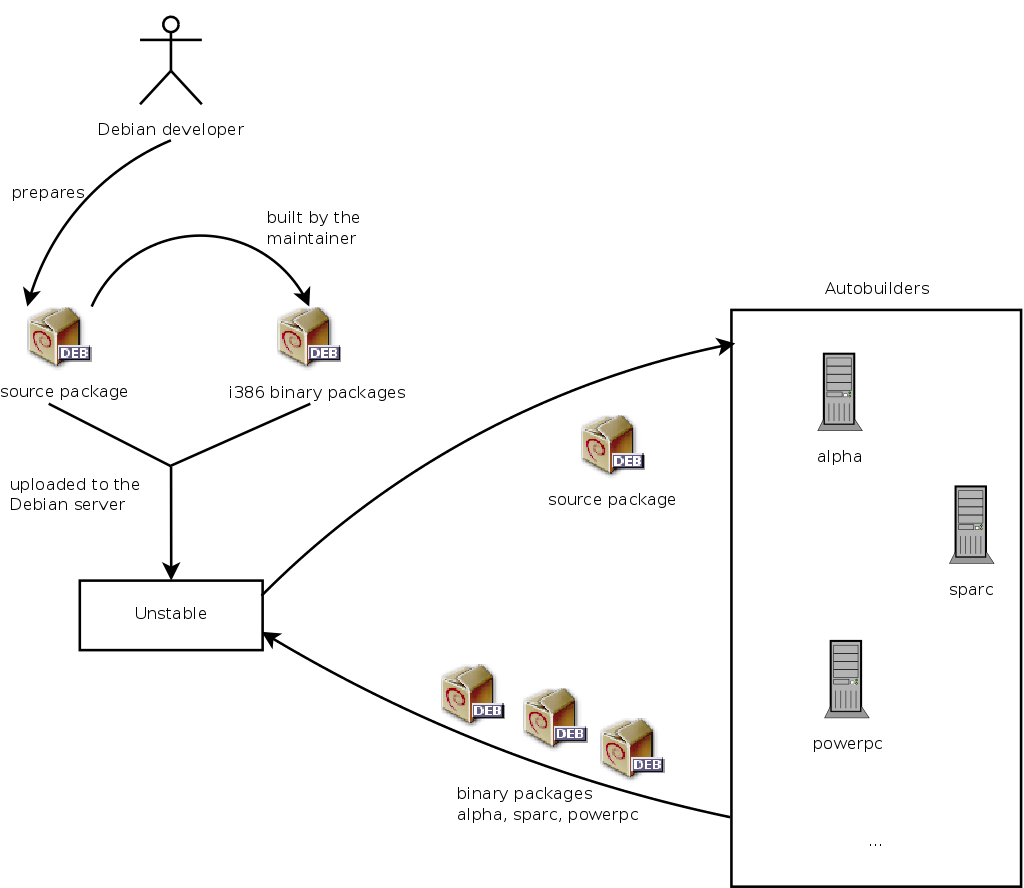
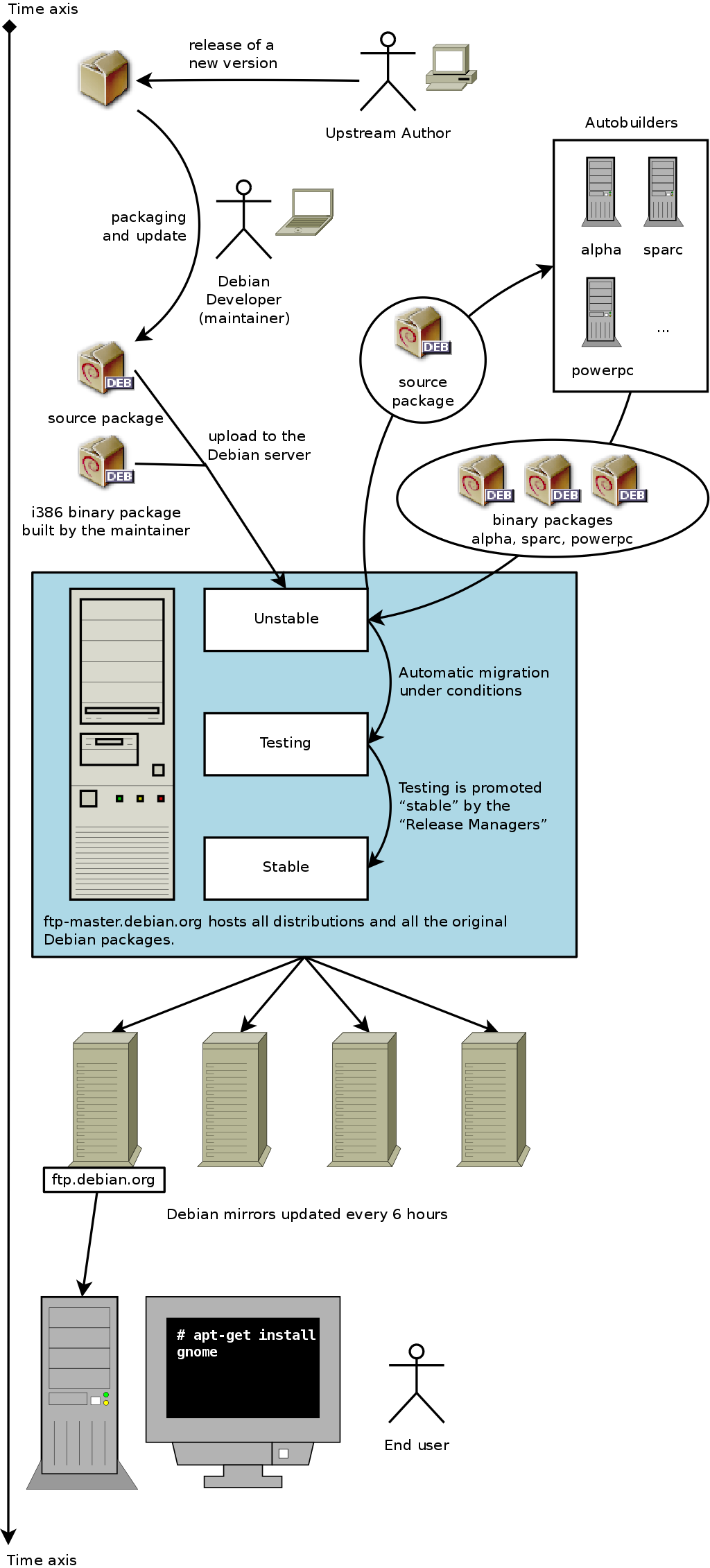
Let us turn back to the case of a typical package. The maintainer creates an initial package, which they compile for the
Unstable version and place on the
ftp-master.debian.org server. This first event involves inspection and validation from the ftpmasters. The software is then available in the
Unstable distribution, which is risky, but chosen by users who are more concerned with staying close to the cutting edge, with more up to date packages, than they are worried about serious bugs. They discover the program and then test it.
If they encounter bugs, they report them to the package's maintainer. The maintainer then regularly prepares corrected versions, which they upload to the server.
Every newly updated package is updated on all Debian mirrors around the world within less than six hours. The users then test the corrections and search for other problems resulting from the modifications. Several updates may then occur rapidly. During these times, autobuilder robots come into action. Most frequently, the maintainer has only one traditional PC and has compiled his package on i386 architecture (or amd64); the autobuilders take over and automatically compile versions for all the other architectures. Some compilations may fail; the maintainer will then receive a bug report indicating the problem, which is then to be corrected in the next versions. When the bug is discovered by a specialist for the architecture in question, the bug report may come with a patch ready to use.
1.5.3. Migration to Testing
A bit later, the package will have matured; compiled on all the architectures, it will not have undergone recent modifications. It is then a candidate for inclusion in the
Testing distribution — a group of
Unstable packages chosen according to some quantifiable criteria. Every day a program automatically selects the packages to include in
Testing, according to elements guaranteeing a certain level of quality:
lack of critical bugs, or, at least fewer than the version currently included in
Testing;
at least 10 days spent in
Unstable, which is sufficient time to find and report any serious problems;
successful compilation on all officially supported architectures;
dependencies that can be satisfied in
Testing, or that can at least be moved there together with the package in question.
This system is clearly not infallible; critical bugs are regularly found in packages included in
Testing. Still, it is generally effective, and
Testing poses far fewer problems than
Unstable, being for many, a good compromise between stability and novelty.
1.5.4. The Promotion from Testing to Stable
Let us suppose that our package is now included in
Testing. While it has room for improvement, the manager thereof must continue to improve it and restart the process from
Unstable (but its later inclusion in
Testing is generally faster: If it has not changed significantly, all of its dependencies are already available). When it reaches perfection, the maintainer has completed their work. The next step is the inclusion in the
Stable distribution, which is, in reality, a simple copy of
Testing at a moment chosen by the Release Manager. Ideally this decision is made when the installer is ready, and when no program in
Testing has any known critical bugs.
Since this moment never truly arrives, in practice, Debian must compromise: remove packages whose maintainer has failed to correct bugs on time, or agree to release a distribution with some bugs in the thousands of programs. The Release Manager will have previously announced a freeze period, during which each update to
Testing must be approved. The goal here is to prevent any new version (and its new bugs), and to only approve updates fixing bugs.
After the release of a new stable version, the Stable Release Manager manages all further development (called “revisions”, ex: 5.0.1, 5.0.2, 5.0.3 for version 5.0). These updates systematically include all security patches. They will also include the most important corrections (the maintainer of a package must prove the gravity of the problem that they wish to correct in order to have their updates included).
End of the journey: Our hypothetical package is now included in the stable distribution. This journey, not without its difficulties, explains the significant delays separating the Debian Stable releases. This contributes, over all, to its reputation for quality. Furthermore, the majority of users are satisfied using one of the three distributions simultaneously available. The system administrators, concerned above all, for the stability of their servers, mock the latest version of GNOME; They can choose Debian
Stable, and they will be satisfied. End users, more interested in the latest versions of GNOME or KDE than in rock-solid stability, will find Debian
Testing to be a good compromise between a lack of serious problems and relatively up to date software. Finally, developers and more experienced users may blaze the trail, testing all the latest developments in Debian
Unstable right out of the gate, at the risk of suffering the headaches and bugs inherent in any new version of a program. To each their own Debian!